3.4. Fleetbench Analysis
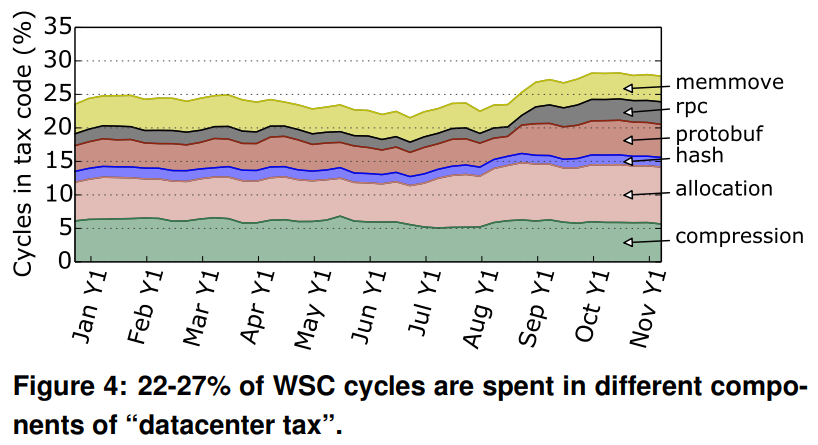
As described in this paper, a significant portion of compute is spent in code common to many applications - the so-called ‘Data Center Tax’. The components that we included in the tax classification are: protocol buffer management, remote procedure calls (RPCs), hashing, compression, memory allocation and data movement.
AWS Configurations -
Intel machine (32 VCPU):m5.8xlargeARM machine (32 VCPU):m6g.8xlargeMachine disk size (gp2):8 GBRegion:us-west-1bRun iterations:5
Analysis -
The analysis is made for the average cpu_time in nano seconds, or for the average bytes_per_second out of 5 iterations.
Compression Benchmark
Covers Snappy, ZSTD, Brotli, and Zlib.
TODO - Add graph.
Hashing Benchmark
Supports algorithms: CRC32, absl::Hash.
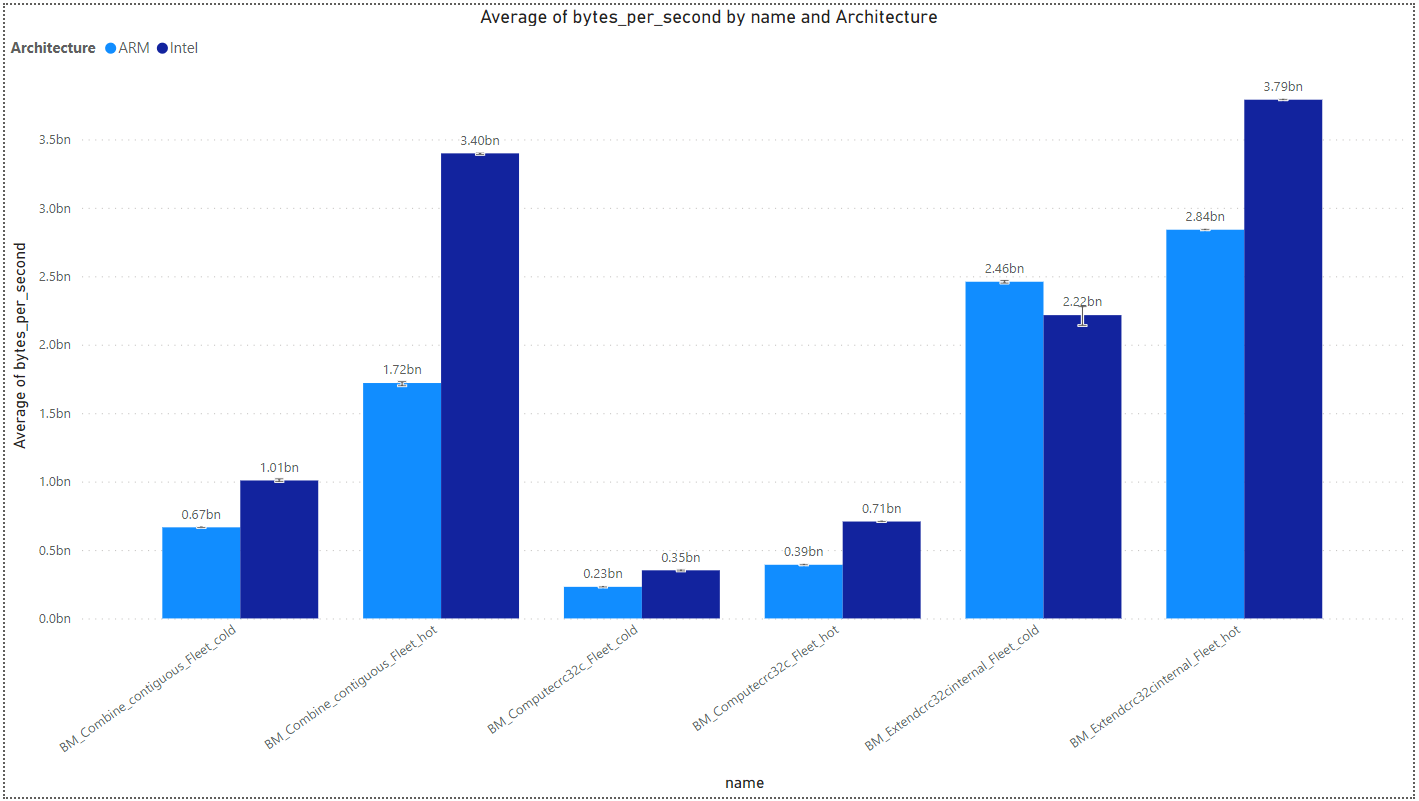
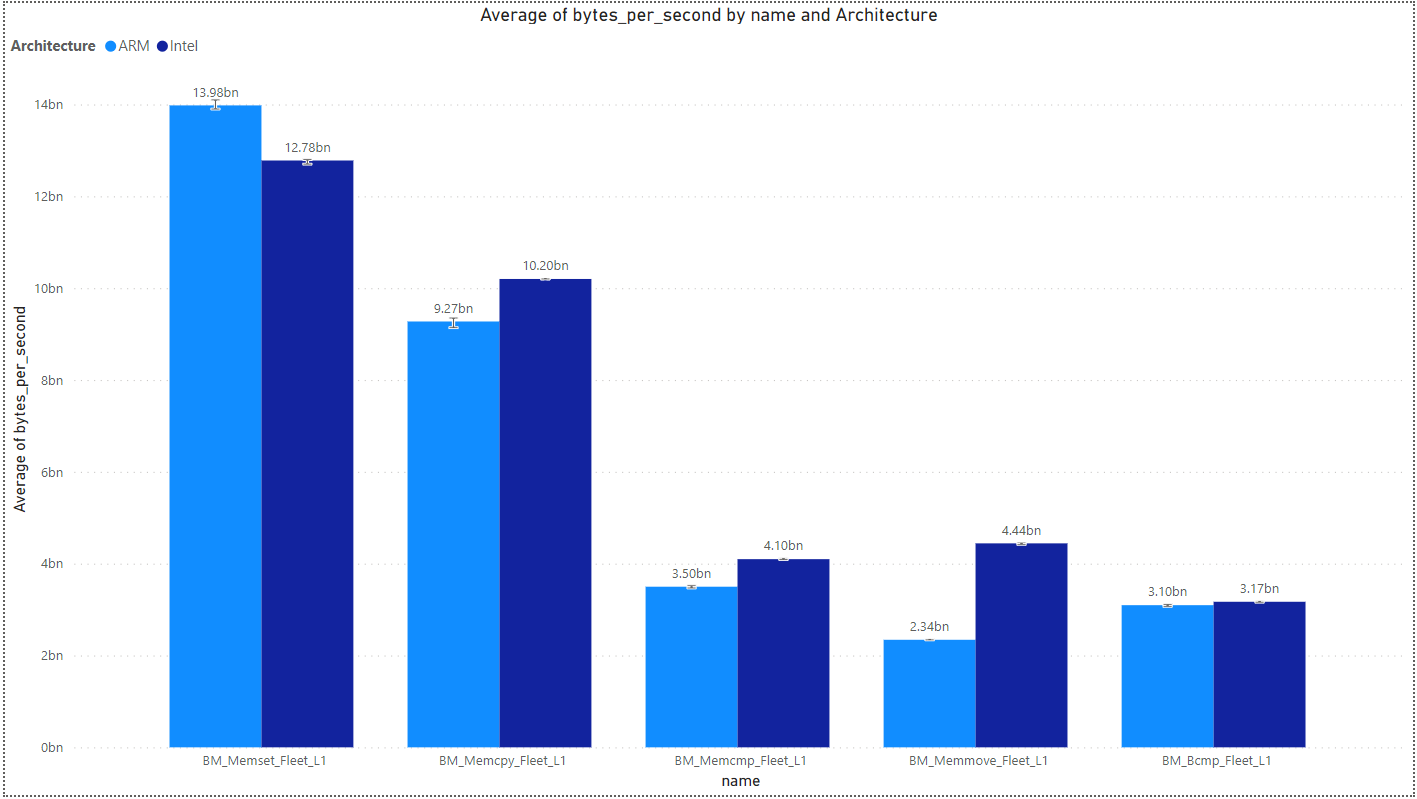
Mem Benchmark
Supports libc algorithms: Memcpy, Memmove, Memcmp, Bcmp, Memset.
Proto Benchmark
Protocol buffers provide a serialization format for packets of typed, structured data that are up to a few megabytes in size. The format is suitable for both ephemeral network traffic and long-term data storage. Protocol buffers can be extended with new information without invalidating existing data or requiring code to be updated. Protocol buffers are the most commonly-used data format at Google. They are used extensively in inter-server communications as well as for archival storage of data on disk. More information can be found here.
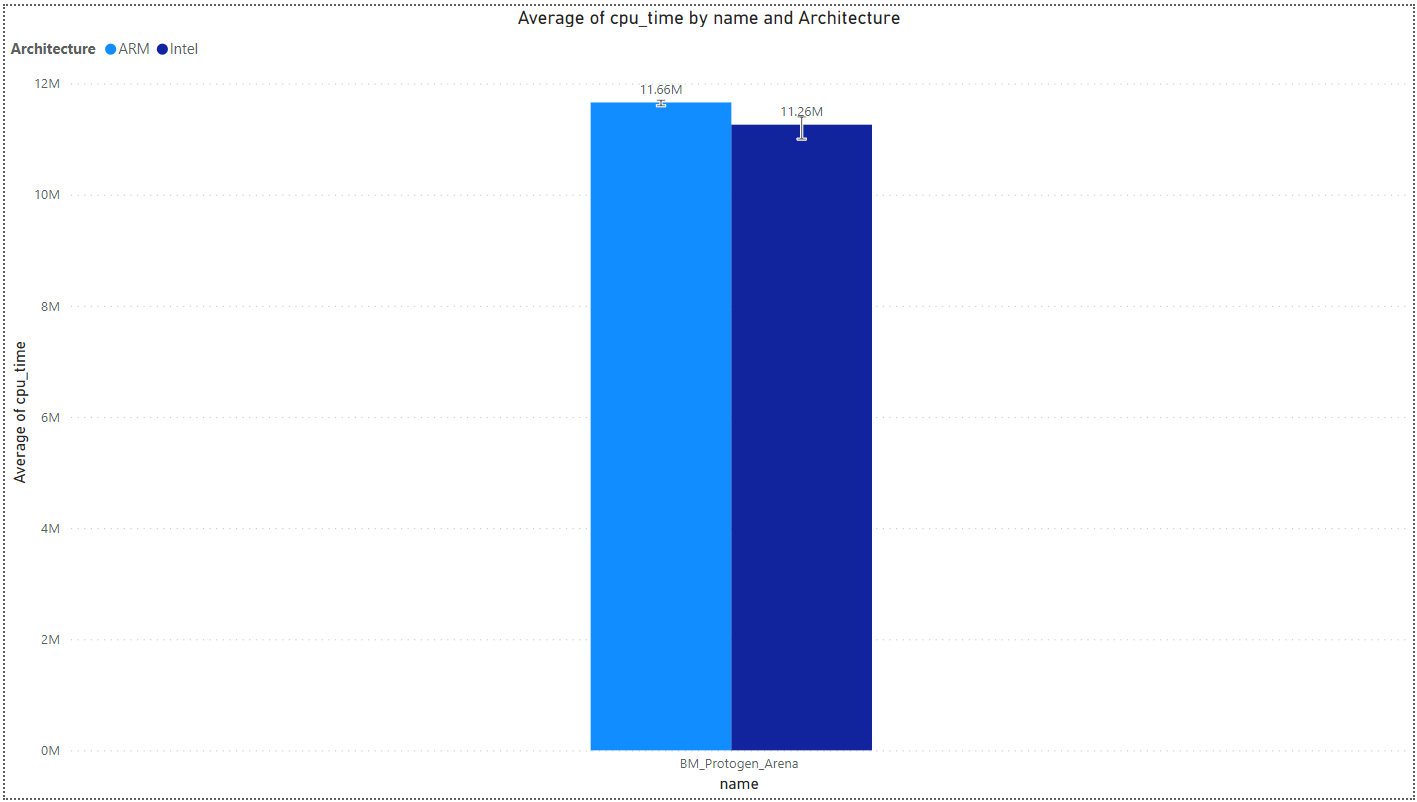
Swissmap Benchmark
Swiss tables hold a densely packed array of metadata, containing presence information for entries in the table. This presence information allows us to optimize both lookup and insertion operations. This metadata adds one byte of overhead for every entry in the table. More information can be found here.
- Swissmap-hot:
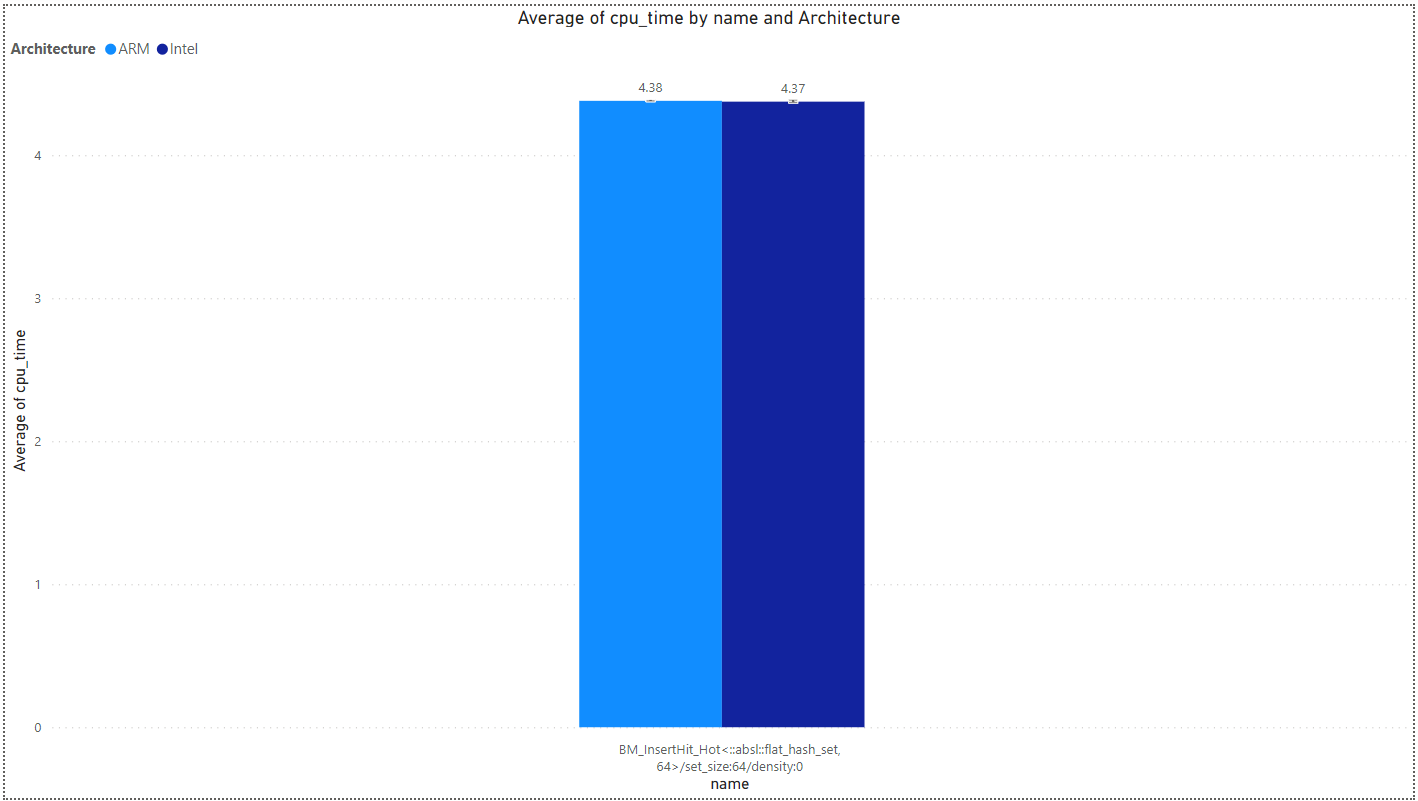
- Swissmap-cold:
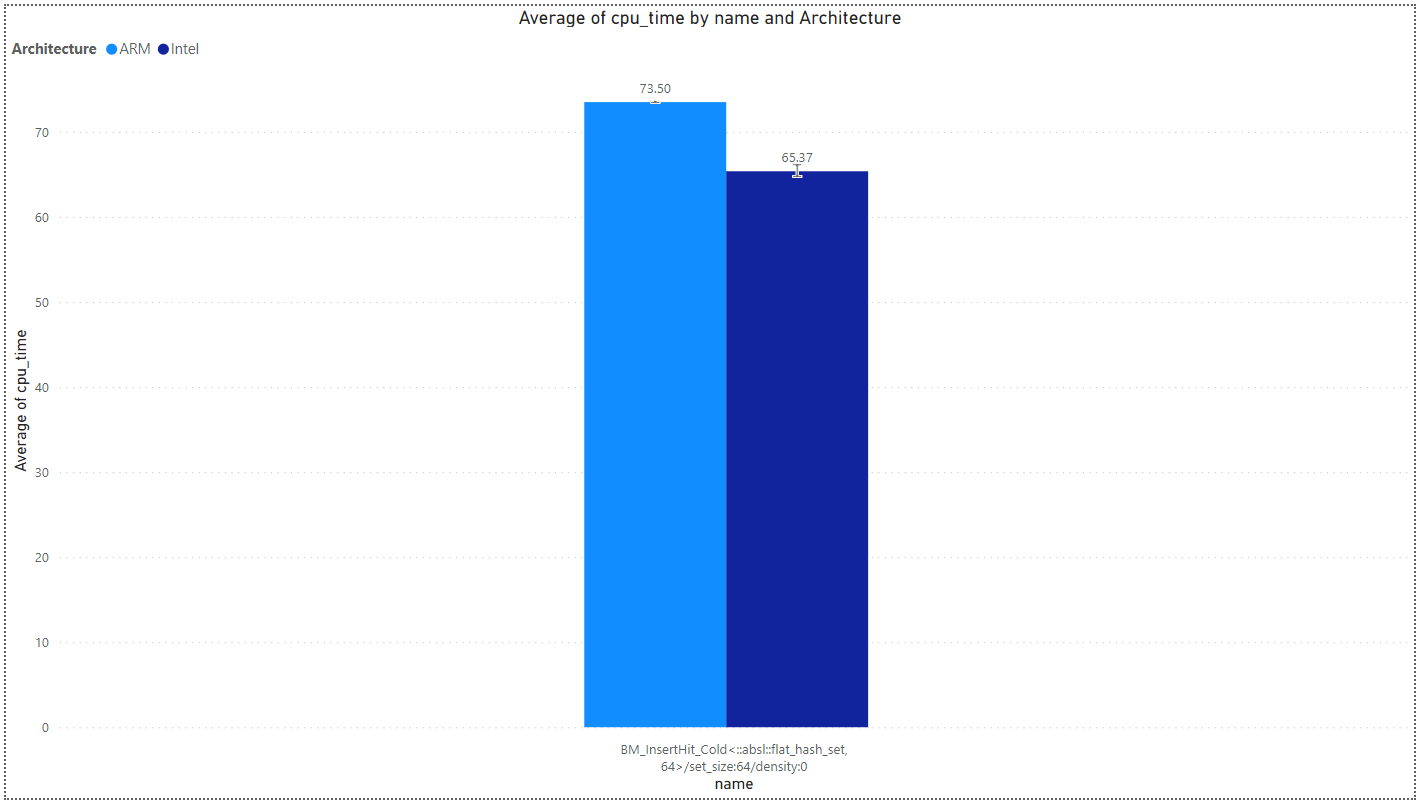
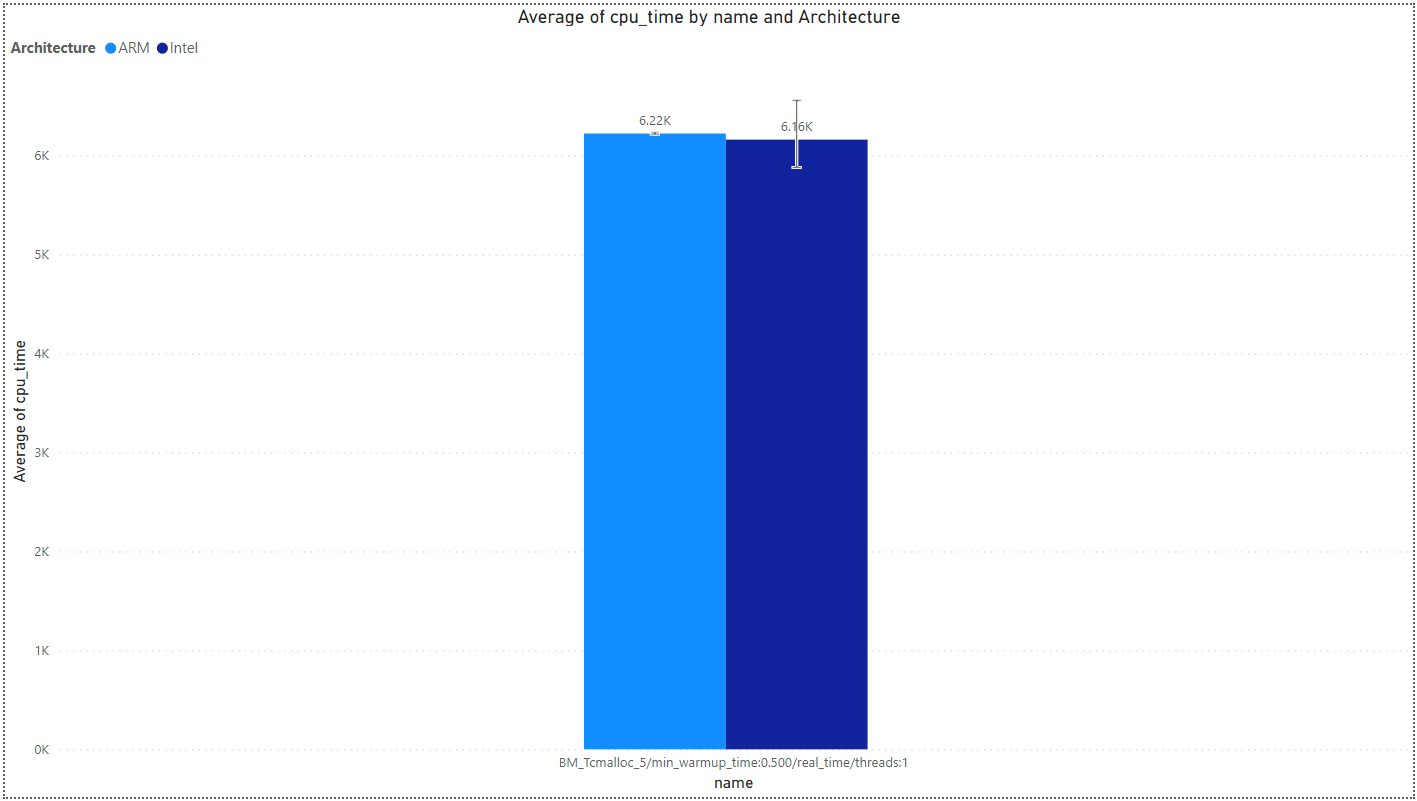
Tcmalloc Benchmark
TCMalloc is Google’s customized implementation of C’s malloc() and C++’s operator new used for memory allocation within our C and C++ code. TCMalloc is a fast, multi-threaded malloc implementation. More information can be found here.