3.2. Multiload Analysis
Multichase - a pointer chaser benchmark.
Multiload - a superset of multichase which runs latency, memory bandwidth, and loaded-latency.
AWS Configurations -
Intel machine (32 VCPU):m5.8xlargeARM machine (32 VCPU):m6g.8xlargeMachine disk size (gp2):8 GBAWS region:us-west-1bRun iterations:5
Analysis -
Analyzing the latency and bandwidth effects of the machines we employed is crucial for gaining a deeper insight into the impediments that hinder the enhancement of their performance.
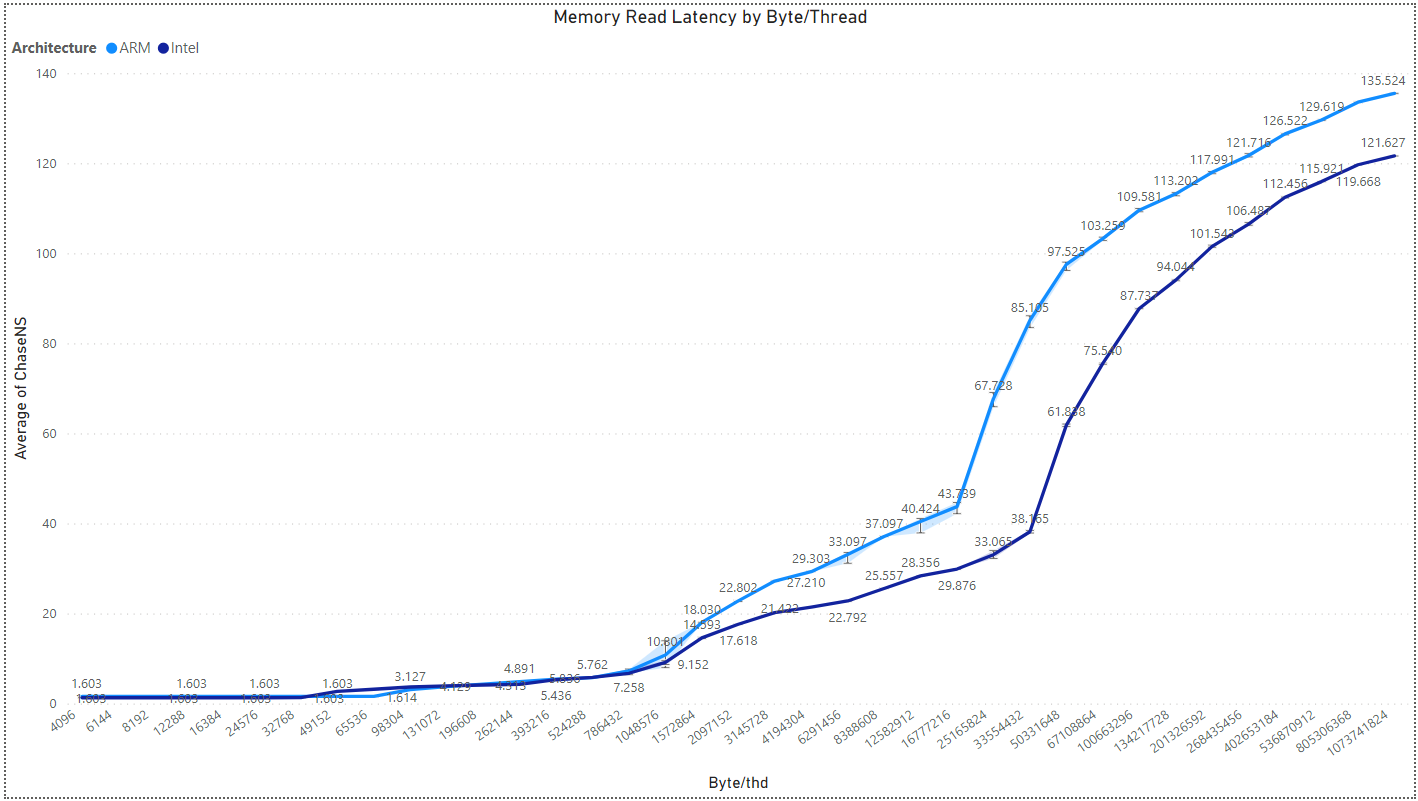
Multichase: Memory Read Latency by Byte/Thread and Architecture
In this benchmark the Multichase “simple” test is running, in which a single thread with variable amount of bytes compute, and measured is the average of ChaseNS (Multichase nano seconds <=> latency) out of 5 iterations.
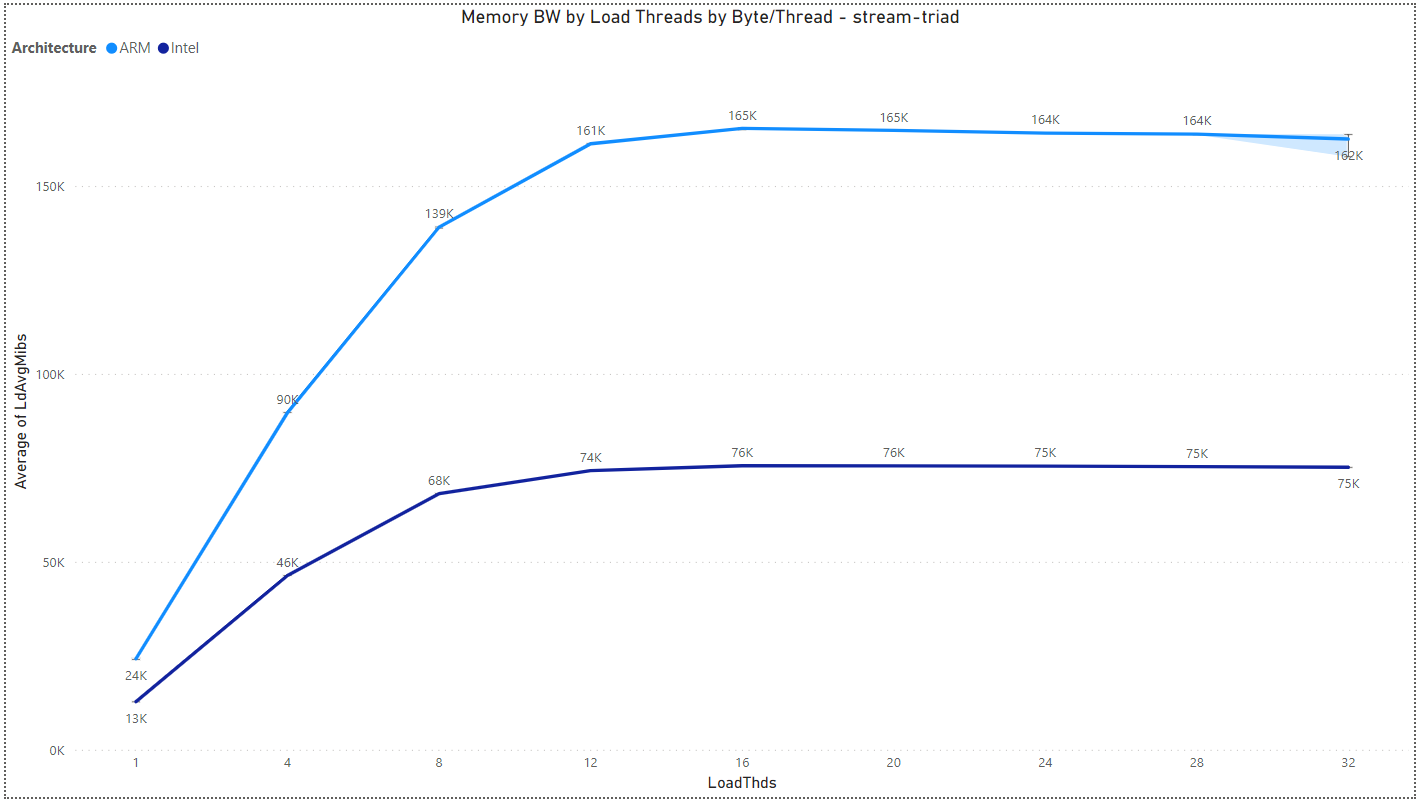
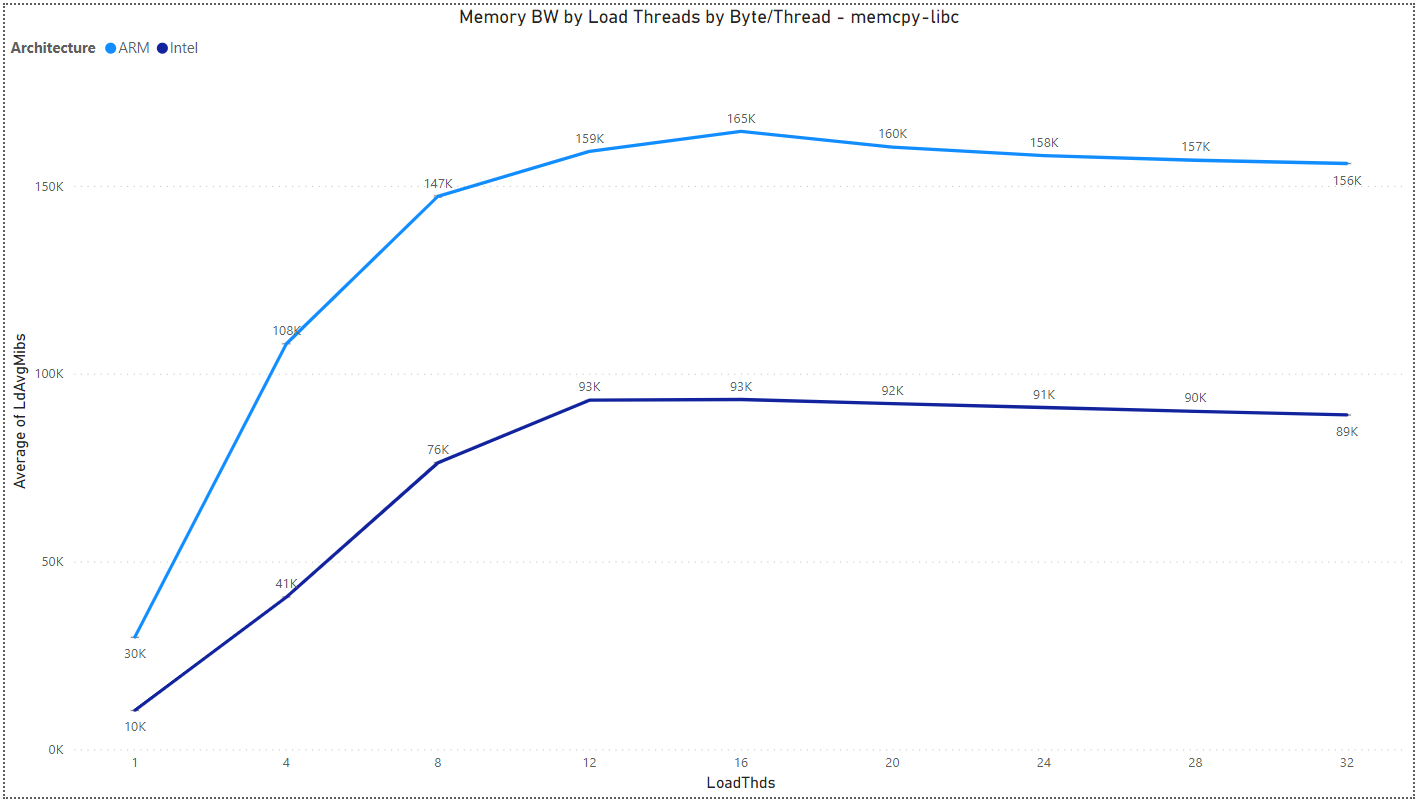
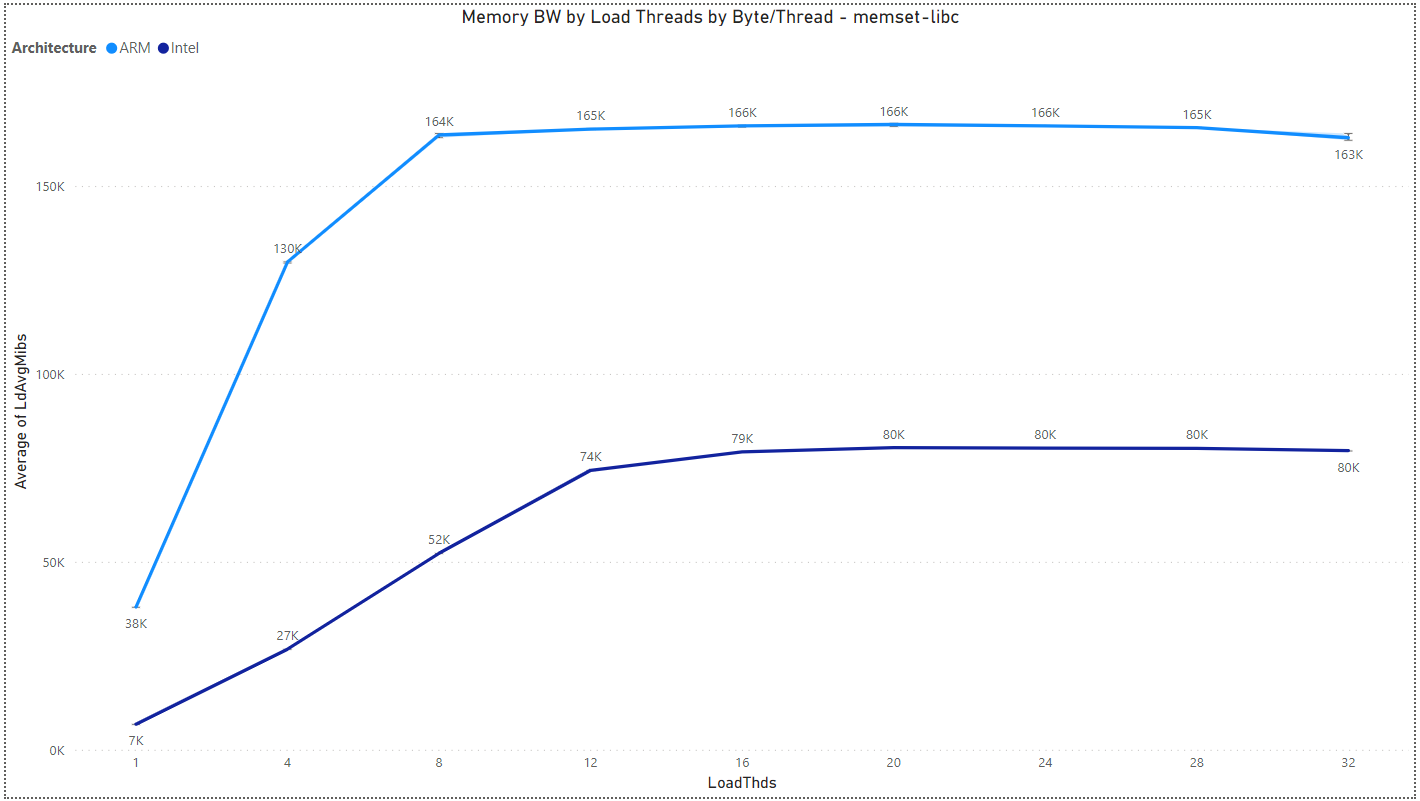
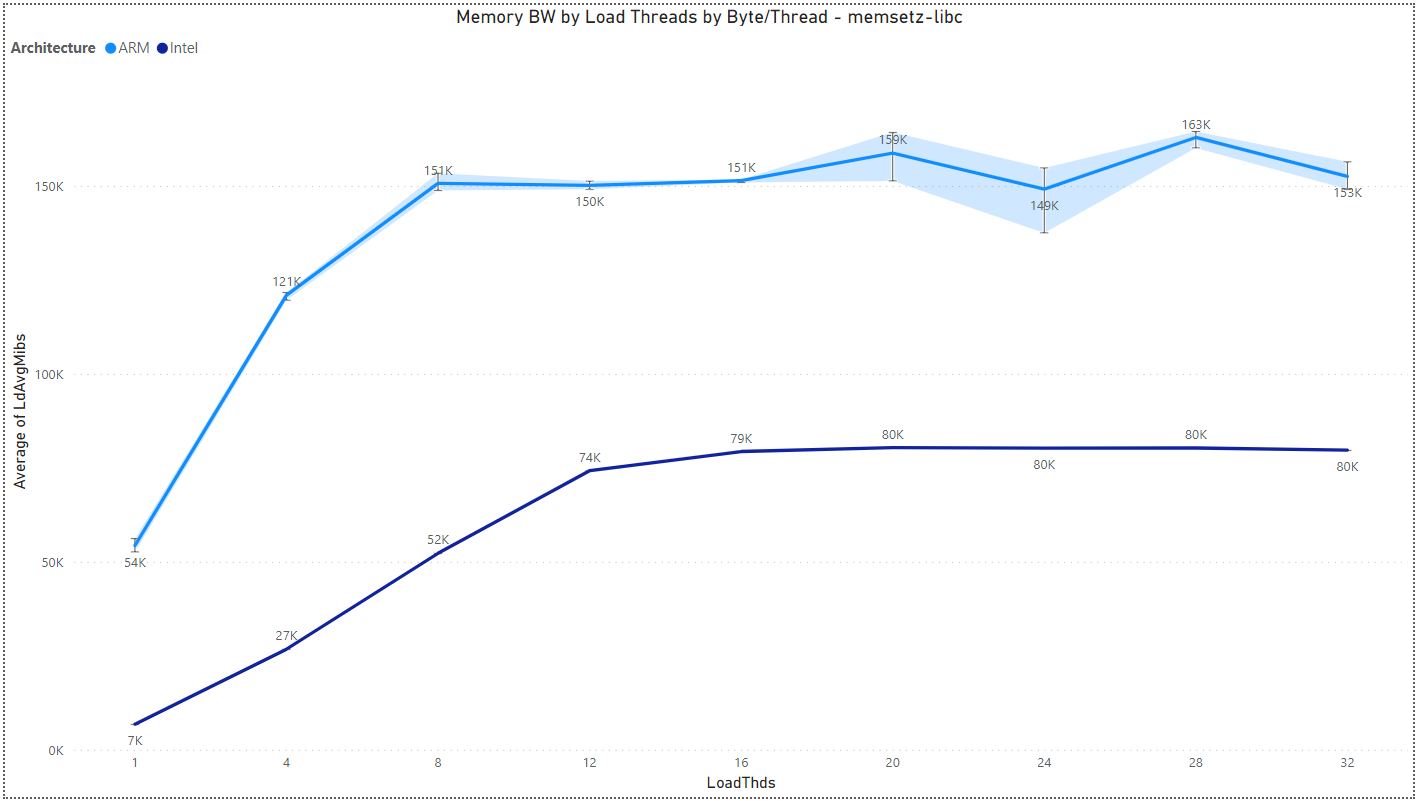
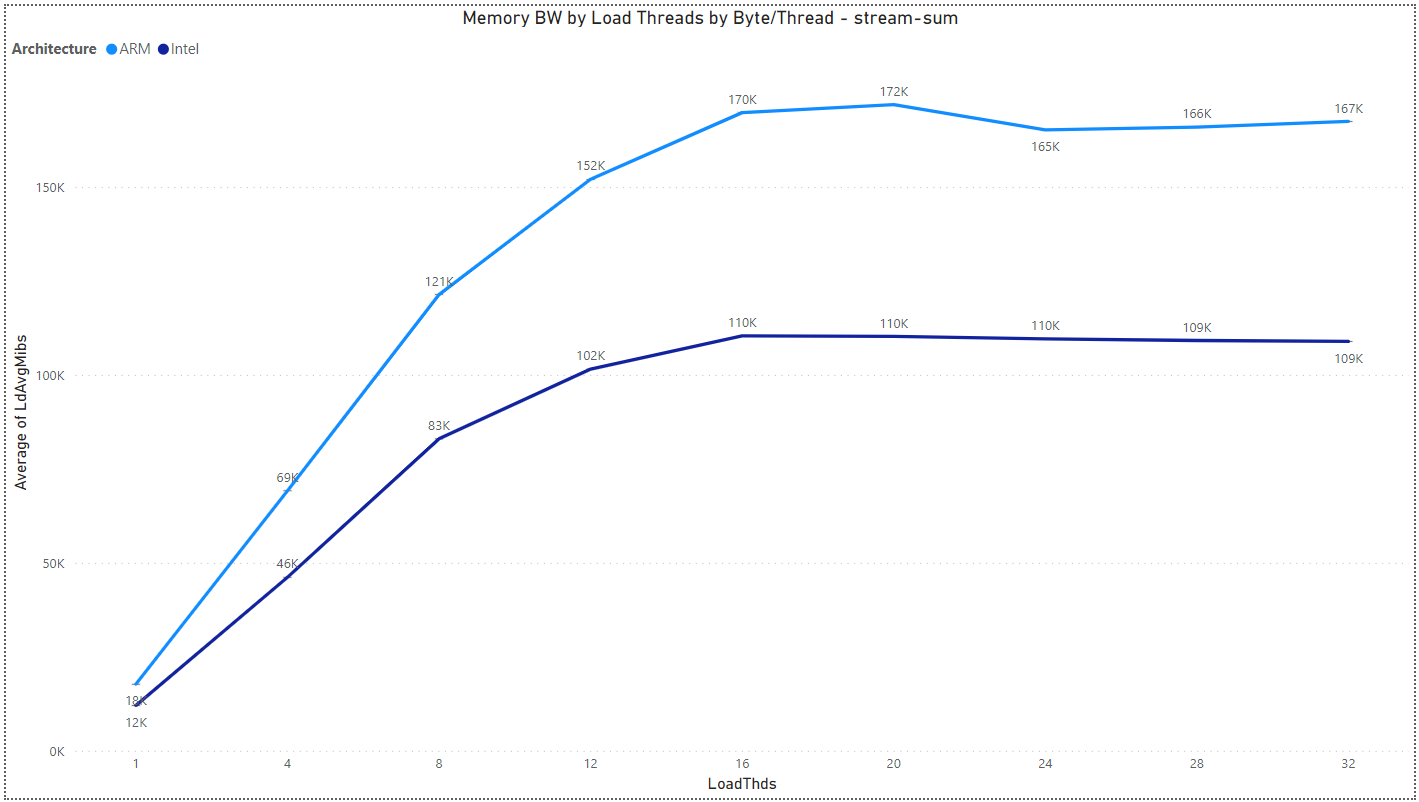
Multiload: Memory BW by Load Threads and Architecture
The results are for Byte/Thread = 1,073,741,824.
- memcpy-libc: 1:1 rd:wr ratio - glibc memcpy()
- memset-libc: 0:1 rd:wr ratio - glibc memset() non-zero data
- memsetz-libc: 0:1 rd:wr ratio - glibc memset() zero data
- stream-sum: 1:0 rd:wr ratio - lmbench stream sum instructions: s+=a[i] (actual binary depends on compiler & -O level)
- stream-triad: 2:1 rd:wr ratio - lmbench stream triad instructions: a[i]=b[i]+(scalar*c[i])