3.1. STREAM Analysis
The STREAM benchmark consists of four main vector operations, each representing a different memory access pattern. The metrics used in STREAM are Copy, Scale, Add, and Triad.
Copy:
- Operation: The Copy operation involves copying the contents of one array to another. It tests the system’s ability to read from one memory location and write to another.
- Formula:
C[i] = A[i] - Description: This operation focuses on testing the memory-to-memory copy performance, representing a scenario where data needs to be duplicated in memory.
Scale:
- Operation: The Scale operation involves multiplying each element of an array by a scalar (constant) value and storing the result in another array.
- Formula:
C[i] = q * A[i] - Description: The Scale operation tests the system’s ability to perform scalar multiplication efficiently, where each element in the array is multiplied by the same constant value.
Add:
- Operation: The Add operation involves adding the corresponding elements of two arrays and storing the result in a third array.
- Formula:
C[i] = A[i] + B[i] - Description: This operation tests the memory bandwidth for reading from two arrays, performing additions, and writing the results to a third array. It represents scenarios where data from multiple sources needs to be combined.
Triad:
- Operation: The Triad operation combines the concepts of Scale and Add. It multiplies each element of one array by a scalar and then adds the corresponding element of another array, storing the result in a third array.
- Formula:
C[i] = A[i] + q * B[i] - Description: The Triad operation is particularly interesting because it involves both multiplication and addition, providing a more comprehensive assessment of the system’s ability to perform combined arithmetic operations on arrays.
For each of these operations, the STREAM benchmark measures the achieved memory bandwidth (in MB/s), indicating how efficiently the system can perform the specified vector operations. By running these operations in sequence, the benchmark provides insights into the sustained memory bandwidth across different types of memory access patterns, helping evaluate the overall memory subsystem performance of a computer system.
AWS Configurations -
Intel machine (32 VCPU):m5.8xlargeARM machine (32 VCPU):m6g.8xlarge
Analysis -
STREAM Memory Bandwidth
- Intel-Xeon-Platinum-8175M Results:
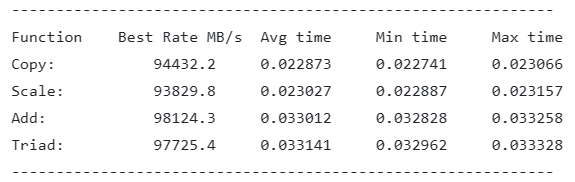
As we can see the peak memory bandwidth is ~76% of the theoretical value presented above.
- ARM Neoverse-N1 Results:
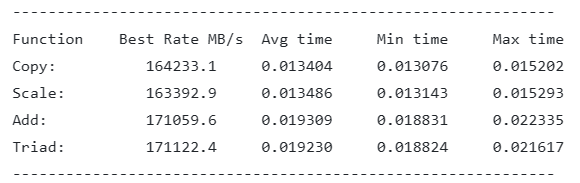
As we can see the peak memory bandwidth is ~83% of the theoretical value presented above.
- Comparison:
ARM Neoverse-N1 (AWS machine m6g.8xlarge) has 60% improved peak theoretical memory bandwidth compared to Intel-Xeon-Platinum-8175M (AWS machine m5.8xlarge), and running the STREAM benchmark we see Neoverse-N1 can reach even ~74% improvement in peak memory bandwidth in practice.